Generate variable voltages using PWM in MicroPython
(Updated at 12/22/2022)
PWM: a trick to generate variable voltages on digital pins
The PWM is a technique that allows generating a voltage between 0 and 3.3V using only digital outputs . PWM is the acronym for Pulse With Modulation . Indeed, this trick is based on the temporal proportion of a logic signal at its high state (3.3V) and its low state (0V): the PWM consists in varying the width of an electrical pulse.
Note
The PWM allows for generating constant voltages during a certain period of time. It does not generate alternating voltages as a DAC could.
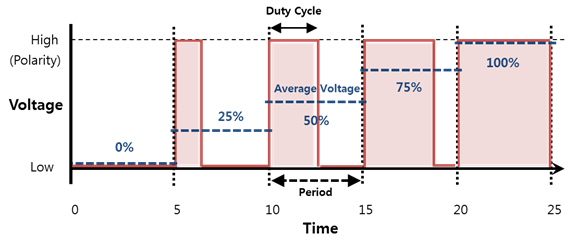
The succession of pulses with a given width is seen on average as a constant voltage between 0V and 3.3V, whose value is determined by :
with \(α\) , the duty cycle (the pulse width in percent)
A PWM signal is configured via the duty cycle and the pulse frequency. We can modify these two parameters in MicroPython.
In practice, PWM is used to :
Controlling the speed of a motor
Controlling the brightness of LEDs
Generate square signals (with α=0.5)
Generate music notes (sound similar to retro consoles)
PWM performance on the ESP32
The microprocessor generates PWM signals not continuously but by dedicated hardware blocks. You only have to configure the PWM blocks once in the script so that the signal is constantly generated in the background. We associate an output of a PWM block to a pin of our board. The processor resources will be free to execute other tasks.
Each PWM block can have an independent frequency.
PWM characteristics of the |
ESP32 |
|---|---|
Frequency range of the PWM signal |
1Hz to 40 Mhz |
Independent PWM frequency |
8 |
PWM output |
16 |
Pulse width resolution |
10 bits |
Note
In most cases, a PWM frequency of around 1000 Hz will be sufficient.
PWM on MicroPython
Using PWM with MicroPython is very simple. MicroPython automatically selects an available PWM block: it is unnecessary to indicate which one you intend to use. The hardware part described above is completely hidden.
The configuration consists in associating a PWM object to a Pin object and choosing the PWM frequency.
from machine import Pin, PWM
pin = Pin(25, mode=Pin.OUT)
pin_with_pwm = PWM(pin) # Attach PWM object on a pin
Note
Since the PWM object is also in the machine module, we can combine the two imports on a single line:
from machine import Pin
from machine import PWM
equals to
from machine import Pin, PWM
Once we have linked a pin of the board to our PWM object, all the functions are done directly on the PWM object (unlike the Arduino code where we specify the pin number with the function analogWrite(pin_number) .
Note
In python, you can insert underscores _ to make the numbers easier to read (and thus avoid counting zeros on large numbers). For example, to write 1 MHz instead of having 1000000 , we can put 1_000_000 .
We use the function .duty_() to select the duty cycle with a value between 0 and \(2^{10}\) (0-1024). The voltage is set directly on the output of the previously selected pin.
To see the voltage variation, you can use the integrated LED of your board with the following script:
from machine import Pin, PWM
LED_BUITLTIN = 2 # For ESP32
pwm_led = PWM(Pin(LED_BUITLTIN, mode=Pin.OUT)) # Attach PWM object on the LED pin
# Settings
pwm_led.freq(1_000)
while True:
for duty in range(0,1024):
pwm_led.duty(duty) # For ESP32
To clarify, you could specify the duty cycle percentage and then apply a formula.
from machine import Pin, PWM
LED_BUITLTIN = 2 # For ESP32
pwm_led = PWM(Pin(LED_BUITLTIN, mode=Pin.OUT)) # Attach PWM object on the LED pin
pwm_led.freq(1_000)
duty_cycle = 50 # Between 0 - 100 %
pwm_led.duty(int((duty_cycle/100)*1024))
We can change the brightness of the LED by varying the duty cycle between 0 and 100%.
from machine import Pin, PWM
import time
LED_BUITLTIN = 2 # For ESP32
pwm_led = PWM(Pin(LED_BUITLTIN, mode=Pin.OUT)) # Attach PWM object on the LED pin
pwm_led.freq(1_000)
while True:
for duty in range(100): # Duty from 0 to 100 %
pwm_led.duty(int((duty/100)*1024))
time.sleep_ms(5)
Note
We add a 5ms delay with time.sleep_ms(5) to slow down the code and see the variation of the brightness with the eye.
Mini-Project: Dimming the ESP32 built-in LED
With all that we have seen, the script is straightforward:
from machine import Pin, PWM
import time
LED_BUITLTIN = 2 # For ESP32
pwm_led = PWM(Pin(LED_BUITLTIN, mode=Pin.OUT)) # Attach PWM object on the LED pin
# Settings
pwm_led.freq(1_000)
while True:
for duty in range(0,1024, 5):
pwm_led.duty(duty)
time.sleep_ms(5)
for duty in range(1023,-1, -5):
pwm_led.duty(duty)
time.sleep_ms(5)
Note
To vary the voltage faster, we change the duty from 5 to 5 with range(0, 1024, 5) . To decrement a value, we put a step of -5 range(1023, -1, -5) .
